Many NAMI Affiliates offer an array of outstanding peer-led programs that provide free education, skills training and support. Discover which education program is right for you.
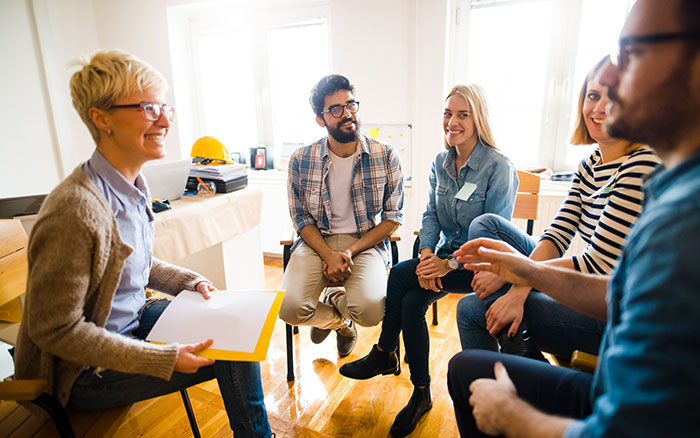


NAMI Connection Recovery Support Group is a free, peer-led support group for any adult who has ..
NAMI Family Support Group is a peer-led support group for any adult with a loved one who has ex..
Los Grupos de Apoyo están disponibles en Español. Ofrecen un ambiente de respeto, comprensión, motivación y esperanza.
NAMI HelpLine is available M-F, 10 a.m. – 10 p.m. ET. Call 800-950-6264,
text “NAMI” to 62640, or email. In a crisis, call or text 988 (24/7).