
December 30, 2019
Reward learning is the subconscious process of adjusting your behavior in response to positive experiences. Past research has shown that people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders (SZ) experience impairments in reward learning, which can cause difficulties in social functioning and relationships. A new study shows that first-degree relatives of people with SZ also experience this impairment compared to people who do not have a family history of SZ. Although further research is needed, this indicates that reward learning patterns are a marker of family risk, rather than a symptom of SZ. To learn more, see the article from Schizophrenia Research.

December 13, 2019
More than 500,000 people go to the emergency department (ED) each year due to deliberate self-harm or thoughts of suicide. A new study linking California ED data with state death records shows that people who presented to an ED with deliberate self-harm had a suicide rate nearly 57 times higher than demographically similar Californians in the year following discharge. Individuals with certain mental health conditions, and particularly individuals who had a firearm injury, were at higher risk. To learn more, visit the NIMH website.

December 2, 2019
Every five years, the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) creates a Strategic Plan for Research. As the lead federal agency for research on mental illness, the NIMH is responsible for guiding and supporting research in basic, translational and clinical science. The Strategic Plan acts as a roadmap to establish their priorities, impacting millions of dollars invested in research grants. The NIMH released a draft of the 2020-2025 Strategic Plan for Research and welcomes comments from the community. To view the draft Strategic Plan, please visit the NIMH website.

November 30, 2019
Super-frequent emergency department (ED) users, people with 18 or more visits per year, often have complex medical, mental health and social needs. However, most strategies used to reduce ED visits focus only on medical needs. To emphasize the importance of a broader perspective, researchers analyzed ED visit data from San Francisco County, CA. The county’s coordinated data system showed that 67% of super-frequent ED users also received mental health treatment, with an average of two psychiatric hospitalizations. These results demonstrate how coordinated data can allow health systems to see the true needs of their populations. To learn more, see the article in Health Affairs.

November 18, 2019
Ketamine has been shown to relieve depressive symptoms within hours of a single intravenous (IV) treatment. To develop a new therapy based on ketamine, researchers must account for potential side effects — especially given the drug’s history of recreational misuse. A new report analyzing data from five clinical trials conducted at NIH over 13 years shows that common side effects of a single IV treatment were mild and lasted only a few hours. This encouraging result supports ongoing research to develop practical, quick-acting antidepressants. To learn more, please visit the NIMH website.

October 12, 2019
Suicide is the second leading cause of death among all people aged 10-34 in the U.S., and a significant concern on college campuses. To better understand risk factors and inform prevention efforts, especially in underrepresented and minority populations, researchers analyzed ten years of data from the Healthy Minds Study. The research shows that suicidal ideation, planning and attempts are more common among students who believe there is significant public stigma against seeking mental health treatment. Risk is also higher among Black students, Asian-international students and sexual minority students. To learn more, please see the article in the Journal of Affective Disorders.
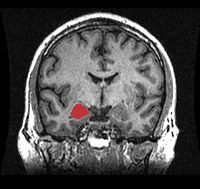
October 2, 2019
The amygdala and the hippocampus — structures in the brain that are involved in emotion, learning and memory — play a role in many of mental health conditions. To learn more about how the amygdala and the hippocampus develop in early life, researchers analyzed brain scans from over 700 participants. The results indicated significant differences in growth trajectories between males and females, which may help explain why conditions develop at different times and at different rates. To learn more, please visit the NIMH website.

October 2, 2019
Over 80% of people with schizophrenia experience auditory hallucination — hearing a sound when there is no external source. This experience can be highly distressing and can contribute to harmful behavior. New research using ultra-high field imaging suggests that auditory hallucinations are related to physical differences in the auditory cortex, an area of the brain that finishes developing very early in life. This could represent a way to identify people vulnerable to schizophrenia before they begin experiencing symptoms. To learn more, please see the article in Nature.
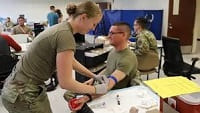
September 25, 2019
An accurate diagnosis is the first step to care and recovery. Diagnosing mental illness can be difficult, however, because symptoms are primarily self-reported. To provide clinicians with an objective screening tool for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), researchers from NYU, Harvard University and the US Army created a biomarker panel that was approximately 80% accurate in identifying PTSD in an initial study. Although the panel requires further testing in a larger population, it is a significant step forward for objective, reliable screening tools for mental health conditions. To learn more, please see the study in JAMA.

September 23, 2019
Genome-wide associate studies show that at least 143 chromosomal sites are involved in the development of schizophrenia. Individually, each site adds only a small fraction of risk — no single gene can explain why schizophrenia is highly inheritable. New research using advanced molecular modelling technology has shown that “expression regulators” can have a much larger impact. Working with specially lab-grown brain cells, researchers have shown that just four genes, when working in tandem, alter the expression of 1,261 others. Understanding this dynamic may help researchers identify which genes are most responsible for risk of schizophrenia. To learn more, please visit the NIMH website.
NAMI HelpLine is available M-F, 10 a.m. – 10 p.m. ET. Call 800-950-6264,
text “helpline” to 62640, or chat online. In a crisis, call or text 988 (24/7).